
Gentamicin is an antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections. This may include bone infections, endocarditis, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis among others. It is not effective for gonorrhea or chlamydia infections. It can be given intravenously, by intramuscular injection, or topically. Topical formulations may be used in burns or for infections of the outside of the eye. It is often only used for two days until bacterial cultures determine what specific antibiotics the infection is sensitive to. The dose required should be monitored by blood testing.

Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of a pyrophosphate group, a pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine.
A salvage pathway is a pathway in which a biological product is produced from intermediates in the degradative pathway of its own or a similar substance. The term often refers to nucleotide salvage in particular, in which nucleotides are synthesized from intermediates in their degradative pathway.
The enzyme 3-ketovalidoxylamine C-N-lyase catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a nucleoside-diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a gentamicin 3'-N-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.60) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a FMN adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [glutamate—ammonia-ligase] adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, nicotinamide-nucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT) (EC 2.7.7.1) are enzymes that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nucleoside-triphosphate-aldose-1-phosphate nucleotidyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phenylalanine adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase (CDS) is the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol from cytidine triphosphate and phosphatidate.

In enzymology, a polynucleotide adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a sulfate adenylyltransferase (ADP) (EC 2.7.7.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
CCA tRNA nucleotidyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name CTP,CTP,ATP:tRNA cytidylyl,cytidylyl,adenylyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Aquayamycin is an anthraquinone derivative. It is an inhibitor of the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase.
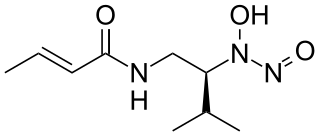
Dopastin is a chemical compound produced by the bacteria Pseudomonas No. BAC-125. It was first isolated and characterized in 1972. It is an inhibitor of the enzyme dopamine β-hydroxylase.
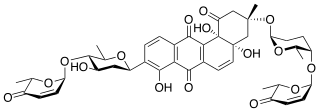
Saquayamycins are "aquayamycin-type" antibiotics isolated from Streptomyces nodosus.
Streptomyces coeruleorubidus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from marine sediment. Streptomyces coeruleorubidus produces the following medications: pacidamycin 1, baumycin B1, baumycin B2, baumycin C1, feudomycin A, feudomycin B, feudomycin C, ficellomycin, feudomycinone A, and rubomycin.

Naphthablin is a naphthoquinone compound with the molecular formula C29H36O8 which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces aculeolatus.









